Form 1099-DIV, Dividends and Distributions Definition
Oct 12, 2024 By Kelly Walker
Are you a financial professional looking for the lowdown on Form 1099-DIV, Dividends, and Distributions? Look no further! This comprehensive blog post will detail what it encompasses, who has to file it, and why it is necessary. This essential form provides important information to taxpayers about their dividend income from stocks or mutual funds.
In addition, we’ll discuss which forms are associated with particular transactions used in filing taxes and how investors use this information to calculate their returns every year. By the end of this article, you will have all the knowledge you need on Form 1099-DIV.
What is Form 1099-DIV, and When Should You File It
Form 1099-DIV is issued by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to taxpayers who receive dividends and distributions from certain investments. Form 1099-DIV includes information about the amount of any dividends or distributions paid throughout the tax year and must be filed with your annual income tax return.
You should file Form 1099-DIV if you've received any of the following types of payments:
- Interest and dividend income from stocks, mutual funds, or other investments
- Capital gain distributions
- Noncash payments such as property or excess contributions
- Qualified dividends
- Nontaxable distributions.
It's important to note that Form 1099-DIV must be filed separately from Form 1040 and must be sent to both the IRS and the taxpayer. Form 1099-DIV should also be attached to Form 2439, which reports undistributed capital gains.
Different Types of Dividends and Distributions

There are several different types of Form 1099-DIV that taxpayers can receive. Form 1099-INT is for reporting interest income, Form 1099-OID is for reporting original issue discount (OID) income, Form 1099-MISC is used to report miscellaneous income, and Form 2439 is used to report undistributed capital gains.
Form 1099-DIV, dividends, and distributions definition also apply to qualified dividends, subject to special tax rates. Qualified dividends are any dividends declared by a corporation or other type of pass-through entity and meet certain requirements set forth by the IRS.
Qualified dividend income is taxed at the lower capital gains rate rather than the ordinary income tax rate. Form 1099-DIV will also list any nontaxable distributions, such as dividends or distributions reported as a return of principal.
How to Report Dividends and Distributions on Tax Forms
Taxpayers must report Form 1099-DIV and any other relevant forms along with their Form 1040 when filing taxes. Form 1040 includes two sections, one for income and the other for deductions.
In the Income section, taxpayers should list all sources of income, including dividends and distributions from Form 1099-DIV. In the Deductions section, qualified dividends may be deducted if they meet certain criteria.
Form 1099-DIV must be attached to Form 2439 when reporting undistributed capital gains. Form 2439 is also used for reporting excess contributions and noncash payments such as property or stock.
Taxpayers should note that Form 1099-DIV only reports income from dividends and distributions. Form W-2, which reports wages and salaries, cannot be used for reporting dividends or distribution income.
Whether you’re an investor or a financial professional, Form 1099-DIV, Dividends, and Distributions Definition can help you to better understand and report your dividend income. Form 1099-DIV reports all sources of dividend income. It can be used to report qualified dividends, noncash payments such as stocks or property and nontaxable distributions.
What Are Qualified Dividends & Nonqualified Dividends
The Form 1099-DIV, Dividends, and Distributions Definition, also applies to qualified dividends subject to special tax rates. Qualified dividends are any dividends declared by a corporation or other pass-through entity that meet certain requirements set forth by the IRS.
Qualified dividend income is taxed at the lower capital gains rate rather than the ordinary income tax rate. Form 1099-DIV will also list any nontaxable distributions, such as dividends or distributions reported as a return of principal.
On the other hand, nonqualified dividends do not qualify for reduced tax rates and are instead taxed as ordinary income. Nonqualified dividends may include those from foreign corporations not qualifying for the reduced tax rate.
It’s important to note that Form 1099-DIV must be filed separately from Form 1040 and must be sent to both the IRS and the taxpayer. Form 1099-DIV should also be attached to Form 2439, which reports undistributed capital gains and excess contributions.
How to Calculate Your Taxable Income from Dividend Payments

Once Form 1099-DIV has been filled out, taxpayers should use the information to calculate their taxable dividend income. Form 1040 includes a line for total dividends and other distributions, on which taxpayers should enter the total amount of their qualified dividends.
Nonqualified dividends are reported on Form 1040 as ordinary income. They should be entered on the line for wages, salaries, tips, and other income. Form 1040 also includes a line for capital gains which should be used to report any qualified dividends that have been taxed at the reduced rate.
Taxpayers should note that Form 1099-DIV does not include information about taxes withheld from dividend payments. Taxpayers must enter the amount of taxes withheld from Form 1099-DIV onto Form 1040.
Form 1099-DIV, Dividends, and Distributions Definition, is essential for accurately understanding and reporting dividend income. Taxpayers should use Form 1099-DIV to report all types of dividends and distributions and Form 2439 when reporting undistributed capital gains.
Form 1040 should also be used to calculate taxable income from dividends and distributions, including both qualified and nonqualified dividends. Understanding Form 1099-DIV is the first step in accurately filing taxes on dividend income.
FAQs
What is Form 1099-DIV dividends and Distributions?
Form 1099-DIV is a form used to report income from dividends and distributions. Form 1099-DIV includes information about qualified dividends, which are subject to special tax rates, as well as nontaxable distributions and excess contributions.
Where can I find Form 1099-DIV?
Form 1099-DIV can be found on the IRS website. Form 1099-DIV must be sent to both the taxpayer and the IRS.
Is 1099-Div taxable income?
Yes, Form 1099-DIV is taxable income. Form 1040 should be used to report the total amount of qualified dividends and other distributions. Nonqualified dividends should be reported as ordinary income on Form 1040. Taxpayers must also enter any taxes withheld from Form 1099-DIV onto Form 1040.
Conclusion
Accurate and timely filing of the 1099-DIV, Dividends and Distributions form is key to avoiding potential IRS audits or enforcement action. Financial professionals should be mindful that all relevant dividend & distribution information must be reported on this tax form to comply with regulations set by governing bodies. Filing accurately ensures your peace of mind when it comes time for tax season.

What Is a Rebuilt Car Title?

Deciphering Hedge Funds: Balancing Returns and Fees

Understanding Mutual Funds and IPOs Investments

Getting Your Real Estate License

How Are Manufacturing Expenses Vary From Production Costs

How a High P/B Ratio Correlates to High ROE
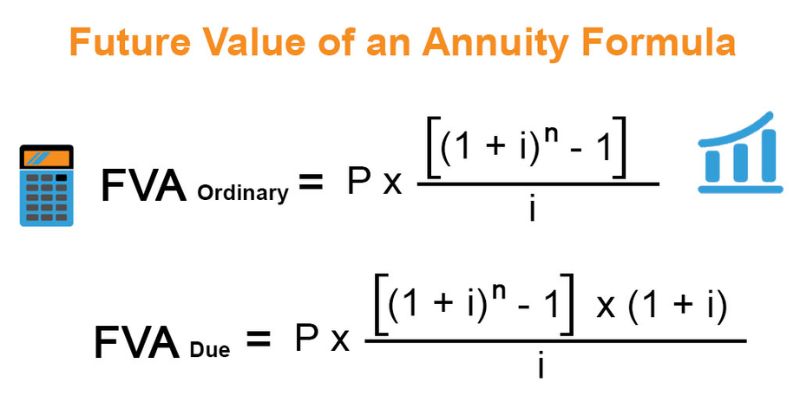
Calculating Present and Future Value of Annuities

What Is an IPO Lock-Up?

What Is a Due From Account?

